|
Location of ectopic
pregnancy |
Ultrasound |
|
|
75-80% very
rare |
Ampullary portion of tube. Ectopic pregnancy in a
cesarean section scar (4) |
EP
close to ovary Gestational
sac in the anterior part
of the isthmic portion of the uterus |
|
|
||
|
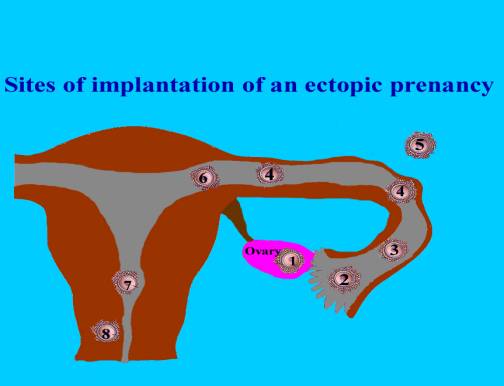
1 – Ovarian ectopic 2 -
Fimbrial end of tube 3 – Ampullary ectopic 4 – Ectopic implantation in proximal or mid
portion of the tube. 5 – Abdominal ectopic 6 – Interstitial ectopic 7 – Implantation at internal cervical os 8 – Cervical ectopic |
||
* Decidual reaction at the site of implantation is uncommon.
* Products of conception may grow on the mucosal or serosal surface of the
fallopian tube or in a mixed position.
* Distortion and expansion of fallopian tube is caused by bleeding into the
wall and lumen rather than from the products of conception.
REFERENCES |
- Breen JL. A 21 year survey of 654 ectopic pregnancies. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1970;106:1004-1019.
- Senterman M, Jiboth R, Tulandi T. Histopathologic study of ampullary and isthmic tubal ectopic pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1988;159;939-941.
- Atri M, Leduc C, Gillet P et.al. Role of endovaginal sonography in the diagnosis and management of ectopic pregnancy. Radiographics 1996;16:755-774.
- Seow K –m, Hwang J –L, Tsai Y –l. Ultrasound diagnosis of a pregnancy in a Cesarean section scar. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001’18:547-549,