|
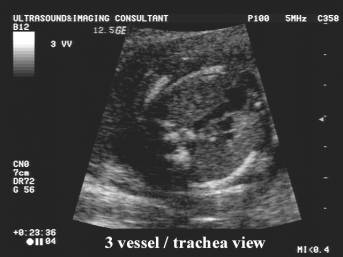
THE THREE VESSEL
(TRACHEA) VIEW |
This view demonstrates the relationship between the
aorta, pulmonary artery and superior vena cava.
This view is obtained by angling the transducer cephalad
from the four-chamber view to the level of the fetal mediastinum.
Vessels assessed include:
·
The
main pulmonary trunk.
·
The
ductus arteriosus.
·
The
aortic arch and isthmus.
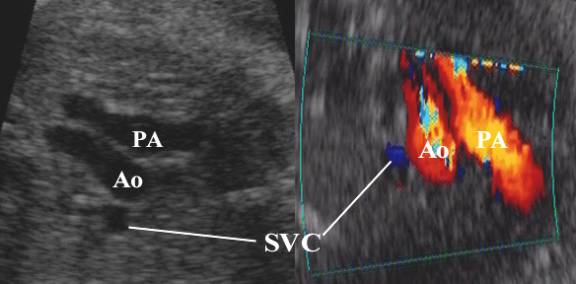
·
The
superior vena cava (SVC) – lies to the right of the aortic arch.
·
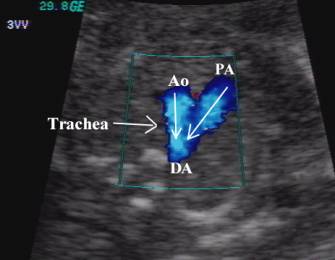
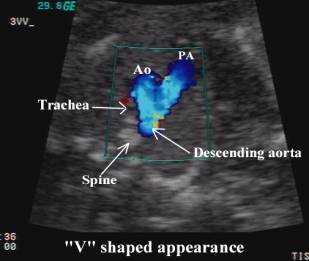
Trachea
– bright walled structure lying to the right of the great vessels and posterior
to the SVC.
|
ULTRASOUND
|
·
Sonographically
convergence of the vessels at the level of the aortic isthmus and ductus
arteriosus is “V-shaped”, with the apex of the “V” lying just anterior to the
fetal spine.
·
The
aortic and pulmonary trunks converge towards the left of the thorax (trachea is
to the right).
|
|
|
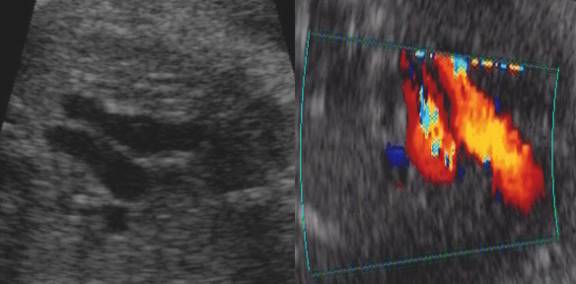
·
Pulmonary
trunk is slightly larger than the aorta (1.2 to 1 ratio).
·
The
vessels run a straight course.
·
Flow
in both vessels are in the same direction (antegrade throughout the cycle) and
are represented by the same color on doppler.
|
|
|
|
·
It is
useful to assess:
o
Size
of the three vessels i.e. whether any vessel is dilated or hypoplastic.
o
Alignment
of the vessels.
o
Arrangement
of the vessels.
o
Whether
all three vessels are present.
o
Whether
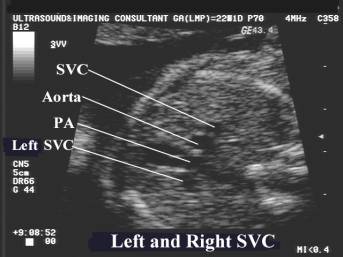
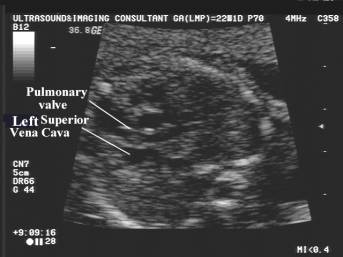
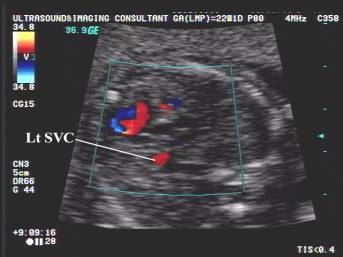
any additional vessels are present e.g. persistent left SVC.
o
Origin
of the pulmonary arteries and whether they are aberrant e.g. arise from the
aorta.
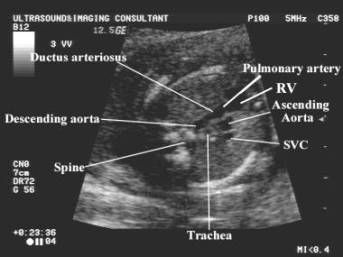
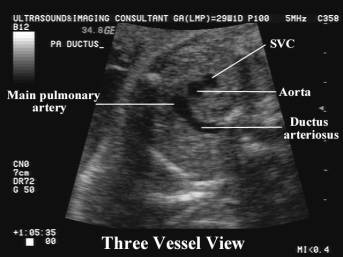

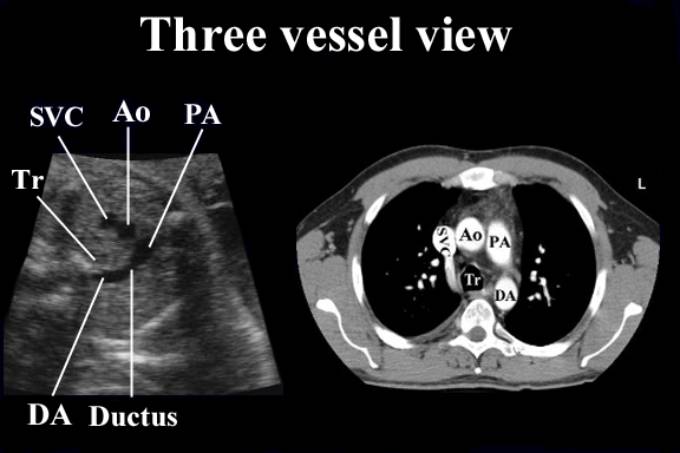
SVC – superior vena cava
Ao – ascending aorta
PA – pulmonary artery
DA – descending aorta
Tr – trachea
·
Small ascending aorta
and large main pulmonary artery (blood diversion from left to right heart):
o
Diminutive
foramen ovale.
o
Dividing
membrane in the left ventricle.
o
Mitral
stenosis / atresia.
o
Left
ventricular outflow tract obstruction.
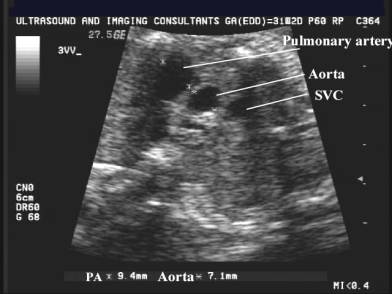

Coarctation of the Aorta - Large PA, small aorta.
·
Large ascending aorta:
o
Aortic
valve stenosis.
o
Aortic
valve regurgitation.
o
Marfan
syndrome.
·
Small main pulmonary
artery:
o
Tetralogy
of Fallot.
o
Pulmonary
atresia with intact ventricular septum.
·
Abnormal alignment of
the vessels.
o
Tetralogy
of Fallot.
o
Double
outlet RV.
o
Interruption
of the aortic arch.
o
Incoprrect
right to left position of the vessels:
§
Complete
transposition of the great vessels.
§
Double
outlet right ventricle.
§
Double
inlet left ventricle.
·
Two vessels instead of
three:
o
Truncus
arteriosus.
o
Pulmonary
atresia with VSD.
·
Four vessels instead of
three:
o
Bilateral
superior vena cava.
o
Tortuous
ductus in late pregnancy.
REFERENCES |
1. Yoo S-J. AJR 1999;172:825-830.