|
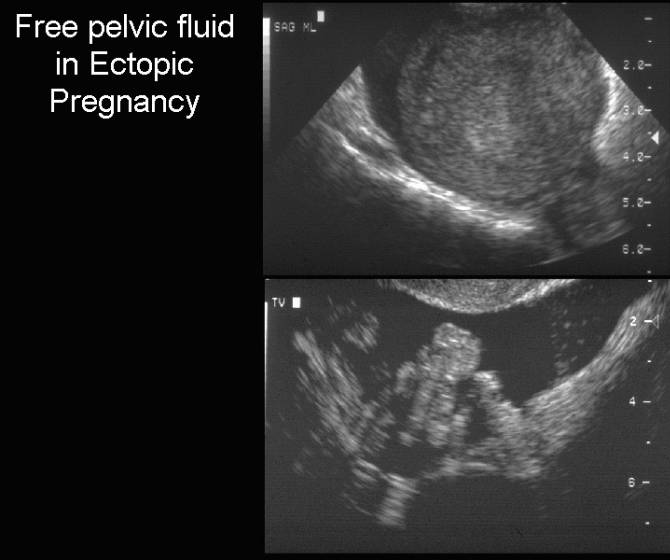
FREE PELVIC FLUID IN
ECTOPIC PREGNANCY |
- May be present in ectopic pregnancies regardless of whether it is intact, ruptured or aborting.
- Non specific finding seen in many other conditions that mimic EP:
- Ruptured ovarian cyst.
- Ovarian torsion.
- PID.
- A bleeding intrauterine pregnancy or normal menstruation may result in the retrograde passage of fluid into the adnexae.
- Seen in 63-70% of EP and 25-31% of intrauterine pregnancies (1,2).
- The amount of fluid in the cul de sac can be semi-quantified
- small = < 1/3 the way up the posterior wall of the uterus (as seen on the longitudinal view)
- moderate = 1/3 - 2/3 the way up the posterior wall of the uterus
- large = > 2/3 the way up the posterior wall of the uterus, or free-flowing intraperitoneal fluid seen in the hepatic or splenic recesses
- Fluid is usually echogenic and may contain particulate matter.
- Large amount of echogenic fluid has a positive predictive value of 86-93% (2)
|
|
|
|
REFERENCES |
- Nygberg DA, Hughes MP, Mack LA, Wang KY. Extrauterine findings of ectopic pregnancy at transvaginal US: importance of echogenic fluid. Radiology 1991;178:823-826.
- Russell SA, Filly RA, Damato N. Sonographic diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy with endovaginal probes: what has really changed. J Ultrasound Med 1993;12:145-151.