|
PLACENTA AND CERVIX |
NORMAL DEVELOPMENT |
- Derived from maternal decidua basalis and fetal chorionic villi.
- First 8 weeks, gestational sac is covered by villi and seen as a diffuse thickening of the echogenic area surrounding the sac.
- 10-12 weeks, those villi not in contact with the decidua basalis involute and the diffuse granular texture of the remaining chorion (frondosum) and decidua basalis can be sonographically visualized.
UTEROPLACENTAL VESSELS |
Link to Uteroplacental vessels
ULTRASOUND |
- Echogenic discoid mass of tissue distinct from the hypoechoic underlying myometrium.
|
|
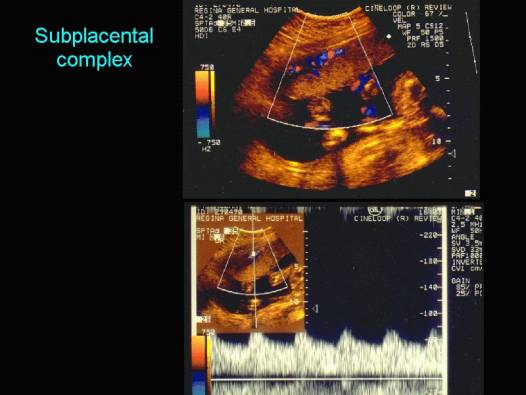
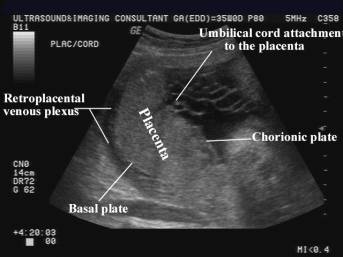
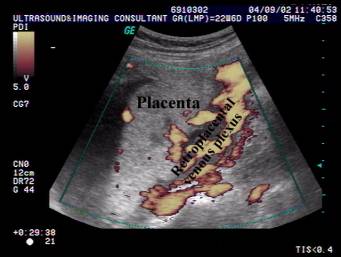
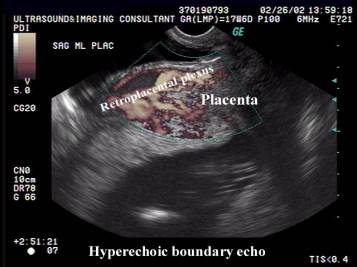
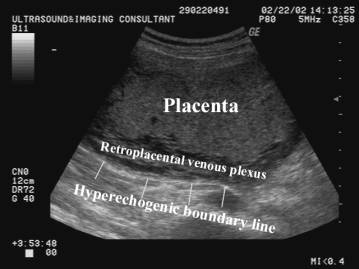
- Subplacental complex is a network of vascular channels sharply delineating the placental-myometrial interphase. Recognition of this interphase avoids false localization of the placenta (near field reverberation artifacts, focal myometrial contractions and fibroids can mimic placental tissue).
|
|
|
|
|
- Placental thickness
- Tables and Graphs of normal thickness rarely exceed 4cm (placentas with small myometrial insertion sites tend to be thicker than those with broad insertion sites).
- Relationship of the placenta to the cervix.
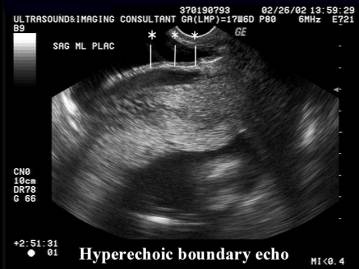
- Normal linear hyperechogeic boundary line (interface between the uterine serosa and posterior bladder wall).
|
|
|
|
|
|
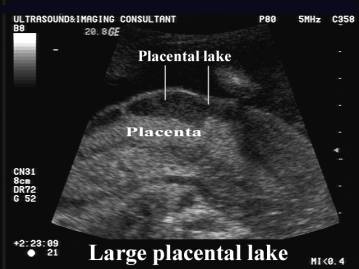
- Placental lake.
|
|
|
- Placental calcification.
- Occurs in normal placental tissue.
- Deposited primarily along the basal plate and along the septa separating placental lobes.
- >50% will have some calcification after 33 weeks.
- Grading.
- Grade 0 = Uniform granular appearance. No visible calcification. Smooth chorionic plate on fetal surface. The placental tissue and basal plate are homogenous. No highly reflective foci (calcifications) are present.
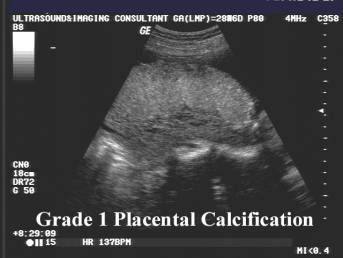
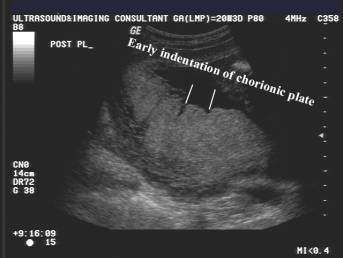
- Grade 1 = Early indentation (undulation) of the chorionic plate. Scattered highly reflective areas (calcification) parallel to the basal plate.
|
|
|
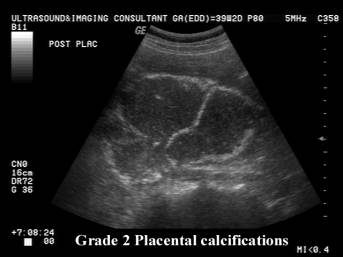
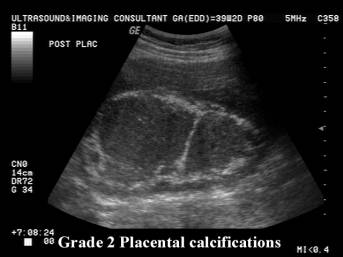
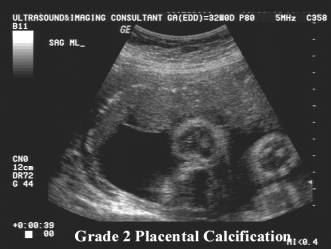
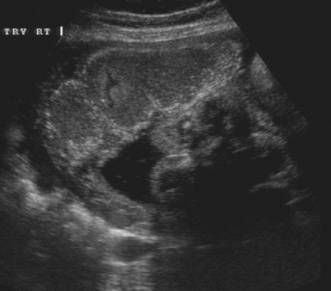
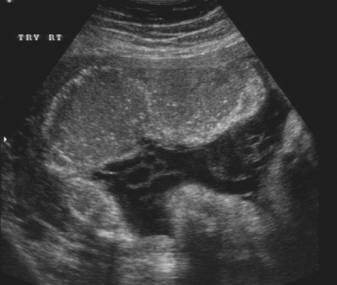
- Grade 2 = Increased basal echogenicities and commalike echogenicities extending into the placenta from indentations of the chorionic plate. Indentations of the chorionic plate do not reach the basal plate, which is well defined by small linear highly reflective areas.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Grade 3 = Extensive basal echogenicities and curvilinear echogenicities extending from the chorionic plate to reach the basal plate (does not reliable indicate fetal lung maturity). This results in the placenta being divided into compartments containing central echo-free areas.
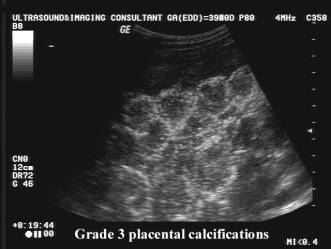
- Recent reports do not support earlier findings that fetal pulmonary maturity evaluated by amniotic fluid lecithin-sphingomyelin (L/S) ratios. Subsequent reports have shown that grade 3 placentas was associated with an immature L/S ratio n 8-42% of cases, and is not accurate enough to replace amniocentesis for predicting pulmonary maturity.
- A randomized controlled study has demonstrated that pregnant women with grade 3 placentas on ultrasound between 34 and 36 weeks have an increased risk of problems during labor, and their babies have an increased risk of low birthweight, intrapartum distress and perinatal death.
Immature Placenta: Grade 0 to 2 with no grade 3.
Intermediate Placenta: Some placental parts graded 3.
Mature Placenta: Entire placenta grade 3.
·
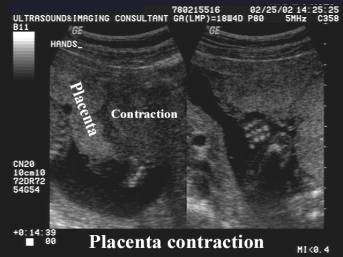
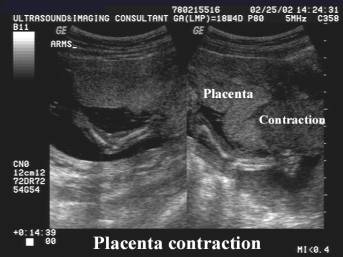
Placental contraction.
|
|
|