|
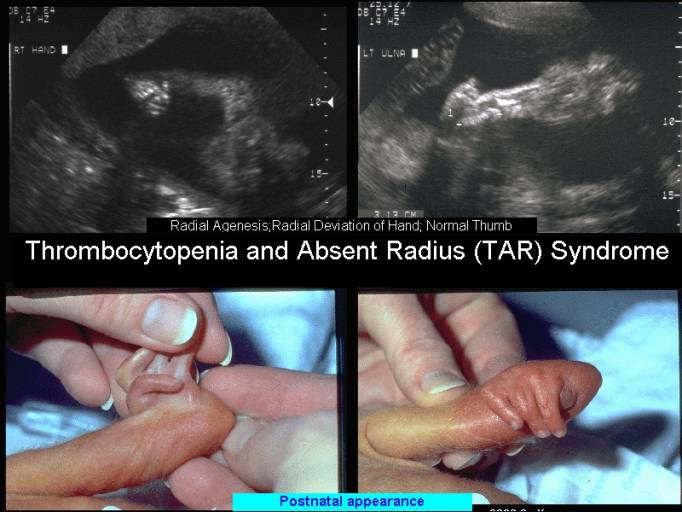
THROMBOCYTOPENIA AND ABSENT RADIUS (TAR)
SYNDROME |
TAR syndrome is a congenital anomaly characterized by:
- Thrombocytopenia (less than 100,000 platelets per mm cubed).
- Bilateral absence of the radius.
- Autosomal recessive inheritance.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY |
The principal defect is thought to absent or arrested development of the
megakaryocyte progenitor cell or a progenitor cell with a maturational defect.
ULTRASOUND |
- Bilateral absence of the radii.
- Normal thumbs (crucial to the diagnosis). If the thumbs are absent, other diagnoses must be considered.
- Radial deviation of the hand.
- The ulna is abnormal (usually shortened and malformed but may be absent bilaterally in 20% of cases and unilaterally in 10% of cases).
- The humerus is abnormal in almost 50% of cases, and absent bilaterally in 5-10% of cases (a five fingered hand arises from the shoulder).
- Asymmetrical limb shortening, abnormalities of the shoulder joint and hypoplasia of the soft tissues of the arm and shoulder have been reported.
- Synostosis of the metacarpal bones.
- Legs are involved in 50% of cases (dislocation of the hips, subluxation of the knees, coxa valga, patella dislocation, tibial tortion, ankylosis of the knee, foot deformities and abnormal toe placement (scrambling of toes).
- Cleft lip/palate.
- Cardiac anomalies (30%). Tetralogy of Fallot, ASD and dextrocardia have been reported.
- Other abnormalities include pancreatic cyst, Meckel's diverticulum.
|
|
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS |
- Roberts Syndrome (no hematological abnormality, severe shortening of limbs and facial anomalies).
- Fanconi's anemia (hematological manifestations appear between 5-10 years of age; absent thumbs and tendency for leukemia).
- Holt Oram syndrome (no hematological abnormality; upper extremity abnormalities, heart defects).
- SC phocomelia (no
hematological abnormality).
- Cornelia
de Lange syndrome (facial defects, growth restriction and mental
retardation).
- Nager
syndrome (mandibular hypoplasia and malformed ears).
- Trisomies
18 and 13.
- VATER association.
PROGNOSIS |
Although TAR syndrome is not uniformly fatal, early prenatal diagnosis is important as the morbidity and mortality associated with this condition may be high.
Therapies include intrauterine platelet transfusion to prevent fetal hemorrhage in labor; a planned atraumatic delivery or termination of pregnancy in the second trimester may be contemplated (5).
REFERENCES |
- MacDonald MR, Schaefer GB, Olney AH et.al. Hypoplasia of the cerebellar vermis and corpus callosum in thrombocytopenia and absent radius syndrome on MRI studies. Am J Med Genet 1994;50:46-50.
- Midro A, Hubert E, Preferansow J et.al. TAR syndrome with orofacial clefting. Genet Counselling 1993;4(3):187-192.
- Hall JG. Thrombocytopenia and absent radius (TAR) syndrome. J Med Genet 1987;24:79-83.
- Labrune PH, Pons JC, Khalil
M et.al. Antenatal diagnosis in three patients with TAR syndrome. Prenat
Diagn 1993;13:463-466.
- Tongsong, Sirichotiyakul S, Chanprapaph P. Prenatal diagnosis of TAR syndrome. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;15:256-258.