|
CONGENITAL BOWING OF
THE TIBIA |
1.
Posteromedial bowing of the tibia and fibula (1-3).
· Tibia and fibula are angulated posteriorly and medially.
· Usually middle or distal third of the shaft.
· Calcaneovalgus deformity (dorsum of the foot touches the lower part of the leg).
· Foot and ankle are normal.
· Always unilateral.
· No side predilection.
· Cause is unknown? Suggested causes include abnormal fetal position or intrauterine fracture, or a primary defect in the embryological development of the lower leg and the tibial or fibular shafts.
· Prognosis is good. There is usually spontaneous, although incomplete correction of the bowing within the first four years of life.
2.
Bilateral congenital shortening and bowing of the long bones.
· May be associated with skeletal dysplasias.
· Larsen’s syndrome (shortening and bowing of the bone is due to dislocation or subluxation of the knees.
· Campomelic dysplasia.
3.
Anterolateral angulation of the tibia (3,4).
· High risk of spontaneous fracture and subsequent pseudoarthrosis of the tibia, fibula, or both.
· Anatomy and position of the foot are normal.
· Strongly associated with neurofibromatosis.
|
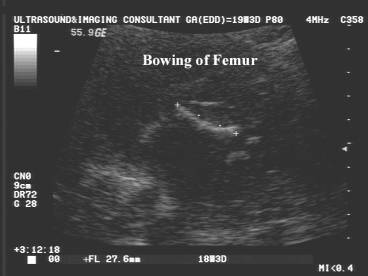
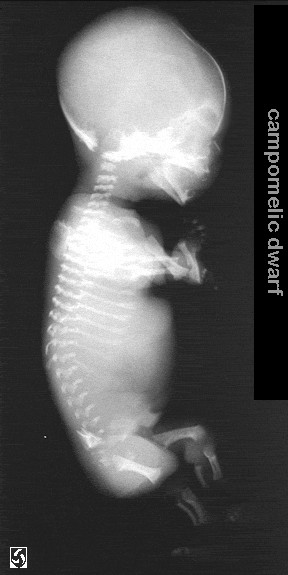
CAMPOMELIC DYSPLASIA
– BOWING OF THE TIBIA |
- Sporadic.
- Autosomal recessive.
ULTRASOUND
|
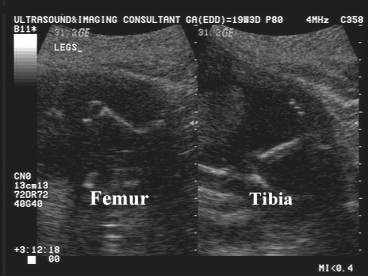
- Bowing of tibia + femur.
- Hypoplastic fibula.
- Macrocephaly, Holoprosencephaly.
- Cloverleaf skull (rarely).
- Micrognathia (90-99%).
- ± Cleft palate.
- Chest and spine.
- Hypoplastic scapulae (92%).
- Narrow bell chest.
- Hypoplastic vertebral bodies.
- Clubfoot.
ASSOCIATED ANOMALIES
|
- Hydrocephalus (23%).
- Congenital heart disease (30%).
- ASD, VSD, Tetralogy of Fallot, Aortic Stenosis.
- Hydrocephalus (30%).
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
|
- Non lethal forms of osteogenesis imperfecta.
- Features favoring a diagnosis of osteogenesis imperfecta
- Arm fractures with callous.
- Cranial compressibility.
- Lack of cranial ossification.
- Variable and asymmetric leg lengths.
- Features favoring a diagnosis of campomelic dysplasia.
- Club feet.
REFERENCES
|
- Papas AM. Congenital posteromedial bowing of the tibia. J Pediatr Orthop 1984;4:525-531.
- Yadav SS, Thomas S. Congenital posteromedial bowing of the tibia. Acta Orthop Scand 1980;51:311-313.
- Zollinger PE, Wessels MW, Wladimiroff JW, Diepstraten AFM. Prenatal ultrasonographic diagnosis of posteromedial bowing of the legs: two case reports. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;15:150-153.
- Adamsbaum C, Kalifa G, Seringe R, Bonnet J-C. Minor tibial duplication: a new cause of congenital bowing of the tibia. Pediatr Radiol 1991;21:185-188.