|
FETAL AKINESIA |
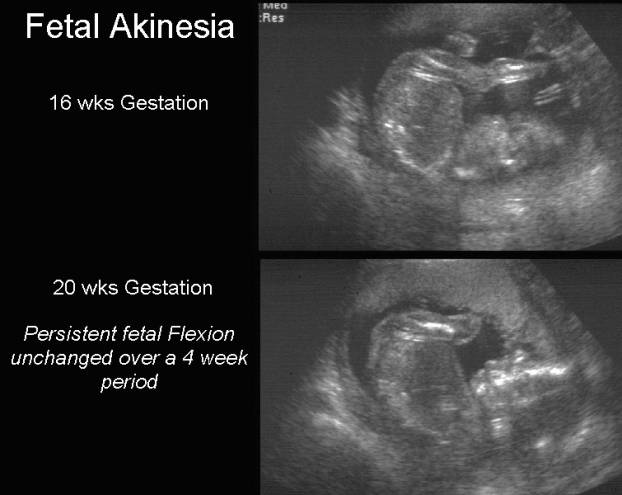
Normal fetal growth and development during pregnancy is dependent on adequate fetal movement. Limitation of movement, regardless of the underlying cause, results in a typical pattern of abnormal fetal morphology. This phenotype has been called the fetal akinesia deformation sequence (FADS).
|
|
ETIOLOGY OF FETAL AKINESIA (1) |
- Neuropathy.
- Myopathy.
- Restrictive dermopathy.
- Teratogens.
- Intrauterine constraint.
PHENOTYPE FINDINGS IN FADS (1,2) |
- IUGR.
- Congenital contractures.
- Limb underdevelopment.
- Pulmonary hypoplasia.
- Abnormal amniotic fluid volume.
- Short umbilical cord.
SYNDROMES ASSOCIATED WITH FADS |
- Pena-Shokeir syndrome.
- Neu Laxova syndrome.
- Neu Laxova variant.
- Restrictive dermopathy.
- Lethal multiple pterygium syndrome.
- Cerebrooculofacioskeletal syndrome
- Oligohydramnios sequence.
- Trisomy 18.
- Arthrogryposis multiplex congenita.
- Gaucher disease type II.
- Congenital myotonic dystrophy.
- Teratogens.
- Congenital infection.
- Alpers progressive infantile neuronal poliodystrophy.
- Fowler syndrome.
REFERENCES |
- Hammond E, Donnenfeld AE. Fetal akinesia. Obstet Gynecol Surv 1995;50(3):240-249.
- Hall JG. Invited editorial comment: Analysis of the Pena-Shokeir phenotype. Am J Med Genet 1986;25:99.