|
PFEIFFER SYNDROME - ACROCEPHALOSYNDACTYLY TYPE V |
- Autosomal dominant inheritance.
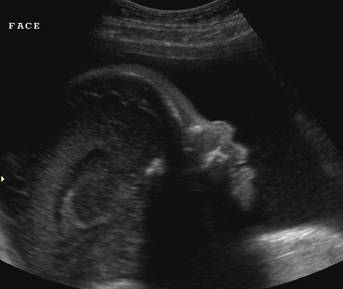
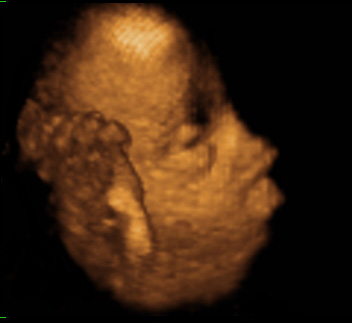
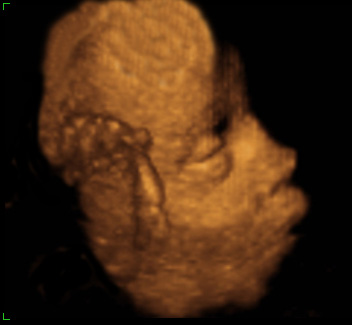
- Originally described in 1964 the syndrome consists of craniosynostosis, midface flattening, beaked nasal tip, ocular proptosis and broad medially deviated thumbs and great toes.
- Genetically heterogeneous. Some cases are linked to mutations at the fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR 1) gene on chromosome 8p11.22-p12. Mutations at the FGFR 2 gene which maps at chromosome 10q25-q26 have also been reported.
CLASSIFICATION (1) / ULTRASOUND (2) |
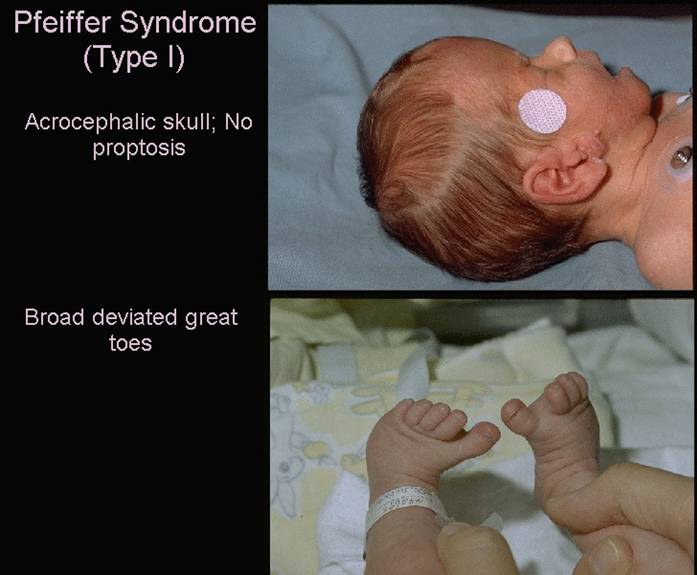
- Type 1 – Craniosynostosis with mild expression. Mild midfacial hypoplasia, little or no ocular proptosis, slightly broadened and minimally deviated thumbs and great toes, syndactyly and normal intelligence.
- Type 2 - Cloverleaf skull deformity and multiple congenital anomalies. Midfacial hypoplasia, ocular proptosis, multiple skeletal anomalies of the extremities (radio-ulnar-humeral synostosis, broad, deviated and contracted thumbs and great toes).
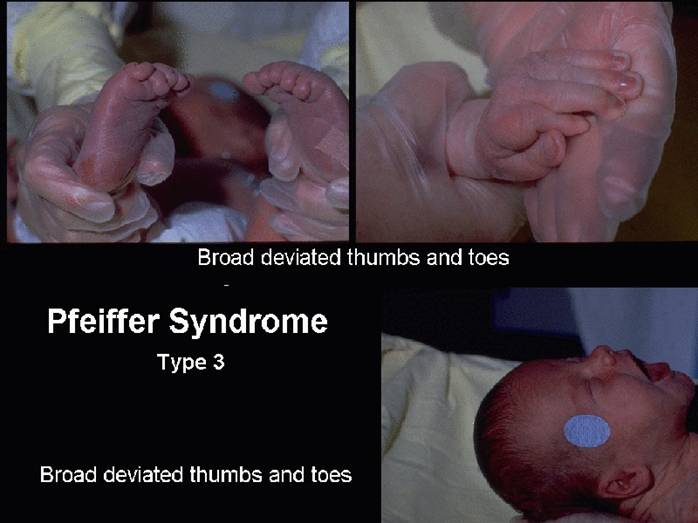
- Type 3 - Similar to type 2, with craniosynostosis but no cloverleaf skull is present.
|
Cranial anomalies |
|
|
Facial
anomalies |
|
|
Hand
and Feet anomalies |
|
|
|
Frontal
bossing Deep nasal
bridge Proptosis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION OF ACROCEPHALOSYNDACTYLY |
Link to
Classification of Acrocephalosyndactyly
REFERENCES |
- Cohen MM Jr. Pfeiffer syndrome update: clinical subtypes and guidelines for differential diagnosis. Am J Med Genet 1993;45:745-750.
- Bernstein PS, Gross SJ, Cohen DJ et.al. Prenatal diagnosis of type 2 Pfeiffer syndrome. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1996;8:425-428.