|
CHOANAL ATRESIA |
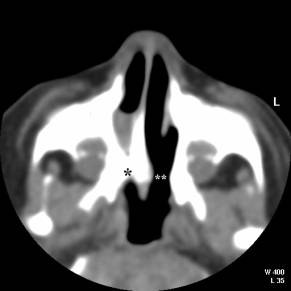
Choanal atresia is a congenital anomaly of the nasal choanae that is usually
diagnosed at birth (respiratory distress in the neonate). There is an
abnormality of canalization (or recanalization) resulting in total or partial obstruction
to the posterior nasal airway.
Classification
The original classification proposed by
Fraser (1):
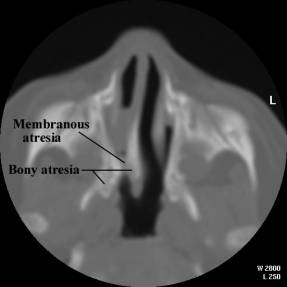
Brown et.al. (2) reviewed the literature and
found no cases of pure membranous atresia.
·
71% mixed
bony-membranous. |
|
Ultrasound
· Diagnosis is usually made at postnatal CT scan ± nasal contrast. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Associated Syndromes
|
|
REFERENCES
|
- Fraser JS. Congenital atresia of the choanae. Br J Med 1910;2:1698-1701.
- Brown OE, Pownell P, Manning SC. Choanal atresia: A new anatomic classification and clinical applications. Laryngodcopy 1996;106:97-101.
- Brown OE, Burns DK, Smith TH et.al. Bilateral posterior choanal atresia: a morphologic and histologic study and computed tomography correlation. Int J Padiatr Otorhinolaryngol 1987;13:125-142.
- Harner SG, McDonald TJ, Reese DF. The anatomy of congenital choanal atresia. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1981;89:7-9.
- Hall BD. Choanal atresia and associated multiple anomalies. J Pediatr 1979;95:395.
- Shashi V, Golden WL, Fryberg JS. Choanal atresia in a patient with the deletion (9p) syndrome. Am J Med Genet 1994;49:88-90.