|
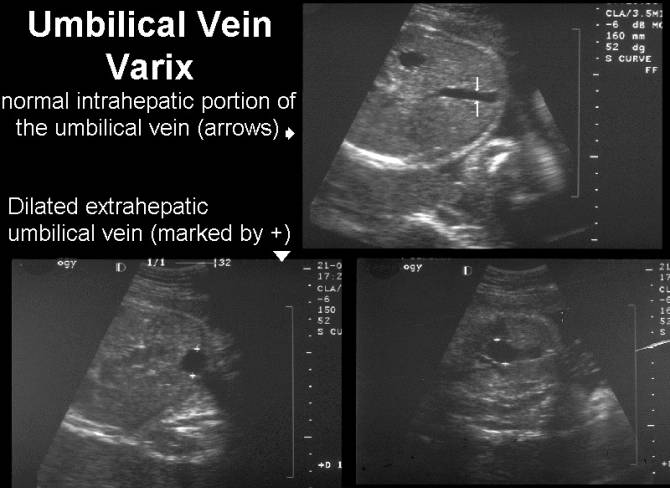
UMBILICAL VEIN
VARIX |
- Uncommon, representing only 4% of malformations of the umbilical cord (1).
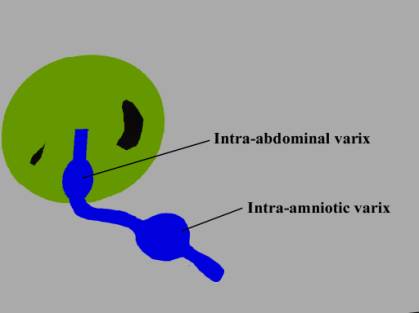
- There are two types which may / may not be associated with malformations:
- Intra-abdominal portion of the umbilical vein and / or umbilical portion of the left portal vein
(i.e. intrahepatic or intra-abdominal extrahepatic)
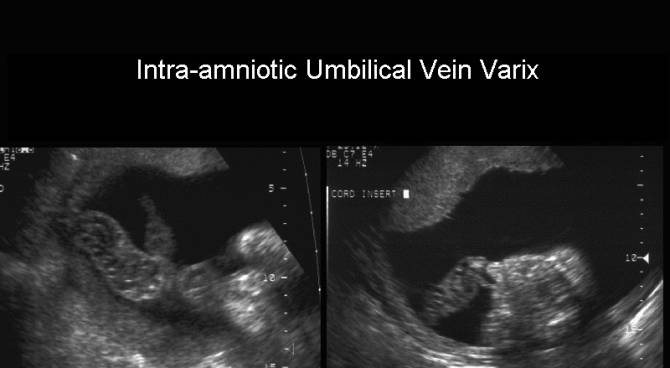
- Intra-amniotic
portion of the umbilical vein.
|
|
|
|
|
|
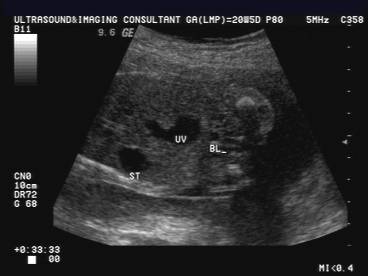
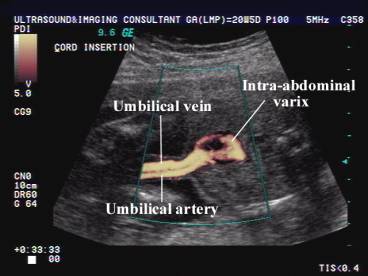
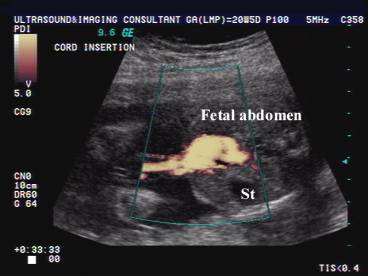
ULTRASOUND OF INTRA-ABDOMINAL VARIX (2) |
- Cystic round or fusiform shaped mass.
- Orientated in an anteroposterior, caudocranial direction.
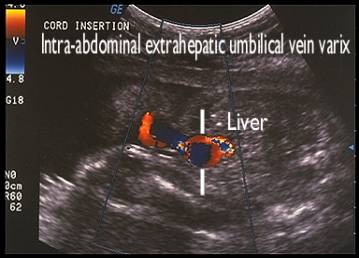
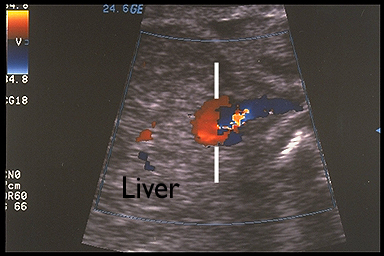
- Located within the substance of the liver (Intrahepatic type).
- Located directly cephalad to the insertion of the umbilical vein into the fetal abdomen.
- Differential diagnosis:
- Choledochal cyst.
- Liver, mesenteric, ovarian or urachal cyst.
- Cystic lymphangioma.
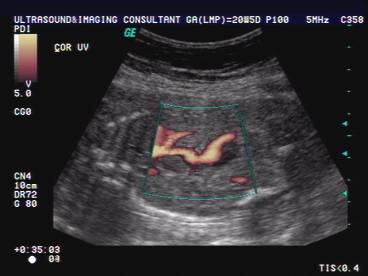
The demonstration of blood flow within the mass on color doppler differentiates the varix from the above cystic masses.
|
Intra-abdomonal
intrahepatic varix |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Intra-abdominal
Extrahepatic varix |
|
|
|
|
ULTRASOUND OF INTRA-AMNIOTIC VARIX |
- Tortuous cystic varix of umbilical vein.
- Detection is enhanced by using color doppler imaging.
- Complications:
- Cord thrombosis (may be seen in 1 in 25 autopsies in fetuses with cord abnormalities) (3).
- Hemorrhage through the amniotic sheath with fetal demise.
|
|
PROGNOSIS |
- Estroff and Bernacerraf (2) - excellent outcome for all five fetuses.
- Mahony and co-workers (4) - nine cases of fetal intraabdominal varix in which four fetuses died and one developed hydrops.
- White and Kofinas (5) - Normal outcome.
- Rahemtullah et.al. (7) – No fetal or neonatal deaths, but a high rate of fetal malformations (chromosomal, syndromes, cardiac defects and diaphragmatic hernia). 34.8% had major congenital abnormalities.
Cardiac decompensation, especially prior to 30 weeks
gestation, has a worse prognosis.
REFERENCES |
- Jeanty P. Fetal funicular vascular anomalies: identification with prenatal ultrasound. Radiology 1989;173:367.
- Estroff JA, Bernacerraf BR. Fetal umbilical vein varix: Sonographic appearance and postnatal outcome. J Ultrasound Med 1992;11:69-73.
- Heifetz S. Thrombosis of the umbilical cord: Analysis of 52 cases and review of the literature. Pediatr Pathol 1988;8:37.
- Mahony BS, McGahan JP, Nyberg DA et.al. Varix of the intra-abdominal umbilical vein: Comparison with normal. J Ultrasound Med 1992;11:73.
- White SP, Kofins A. Prenatal diagnosis and management of umbilical vein varix of the intra- amniotic portion of the umbilical vein. J Ultrasound Med 1994;13:992-994.
- Moore L, Toi A, Chitayat D.
Abnormalities of the intra-abdominal fetal umbilical vein: report of four
cases and a review of the literature. Ultrasound Obst Gynecol 1996;21-25.
- Rahemtullah
A, Lieberman E, Benson C. Outcome of pregnancy after prenatal diagnosis of
umbilical vein varix. J Ultrasound Med 2001;20:135-139.