|
ABNORMAL WAVEFORMS IN
THE UMBILICAL VEIN (1-6) |
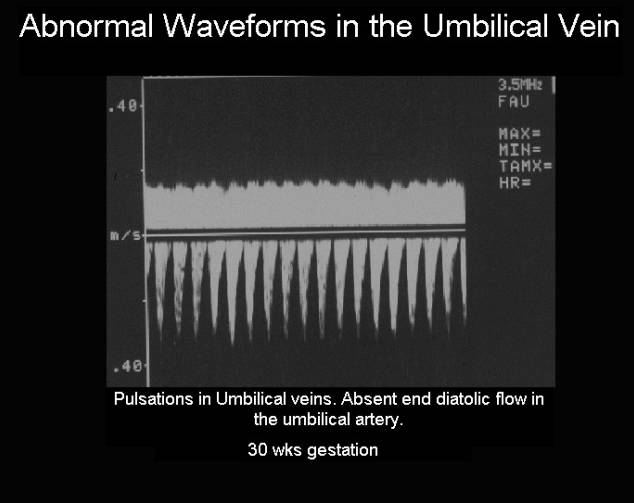
Pulsations in the UV were
defined as a rhythmic reduction in blood velocity of more than 15% of the
baseline velocity.
The pulsations are divided into: a single or double pulsation during one heart cycle, as described by reference 6.
The umbilical vein velocities become pulsatile in the severely growth retarded fetus (1) (pulsations normally disappear by the end of the first trimester).
Pulsations in the
umbilical vein in the second and third trimesters have a high fetal
morbidity and mortality, even in the presence of normal umbilical flow velocity
waveforms (2). Pulsations in umbilical venous flow are known to be a
characteristic sign of fetal heart failure and imminent asphyxia. Double
pulsation is known to be a more severe sign of fetal compromise and a direct
reflection of pulsations in the central veins due to opening of the DV, either
due to hypoxia or increased central venous pressure.
|
|
|
|
TYPES OF PULSATIONS (3-6) |
- Type I Pulsations:
- Decrease the umbilical venous velocity during atrial systole.
- Are transmitted retrograde from the right atrium.
- Are atrial contraction pressure waves which are transmitted from the right atrium back along the venous circulation.
- Compensated fetal congestive heart failure with elevated end diastolic pressure in the right ventricle causes an increase in the reversal of flow during atrial systole in the IVC, hepatic veins, ductus venosus and the umbilical vein.
- Type II Pulsations:
- Decrease the umbilical venous velocity during atrial systole.
- Are not transmitted retrograde from the right atrium.
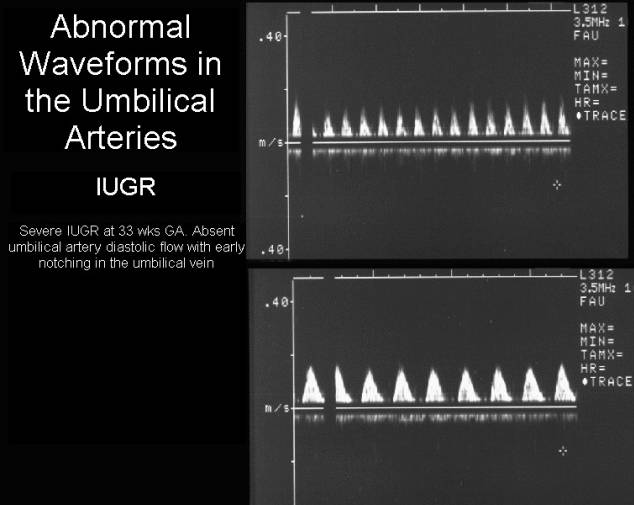
- Are present in the umbilical vein in severe growth restriction.
- Absent end diastolic velocity in the umbilical arteries with normal doppler velocities in the inferior vena cava and ductus venosus.
- Type III Pulsations:
- Augment the umbilical venous velocities in ventricular systole.
- Are caused by cord compression where kinks or entrapment of the cord directly transmits the systolic pulsation to the venous doppler signal. They also may be caused by an umbilical arteriovenous fistula.
|
|
Video clip of umbilical vein notching Video clip of umbilical vein double notching
|
|
|
|
|
|
REFERENCES |
- Nakai Y, Miyazaki Y, Matsuoka Y. Pulsatile umbilical venous flow and its significance. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1992;99:977-980.
- Indik JH, Chen V, Reed KL. Association of umbilical venous with inferior vena cava velocities. Obstet Gynecol 1991;77:551-557.
- Gudmundsson S, Tulzer G, Huhta JC et.al. Venous doppler in the fetus with absent end-diastolic flow in the umbilical artery. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1996;7:262-267.
- Nakai Y, Imanaka M, Nishio J et.al. Umbilical venous pulsation associated with hypercoiled cord in growth-retarded fetuses. Gynecol Obstet Invest 1997;43:64-67.
- Huhta JC. Deciphering the hieroglyphics of venous doppler velocities. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1997;9:300-301.
- Hofstaetter C, Dubiel M, Gudmundsson S. Different types of umbilical venous pulsations and outcome of pregnancy. Early Hum Dev 2001;61:111-117