|
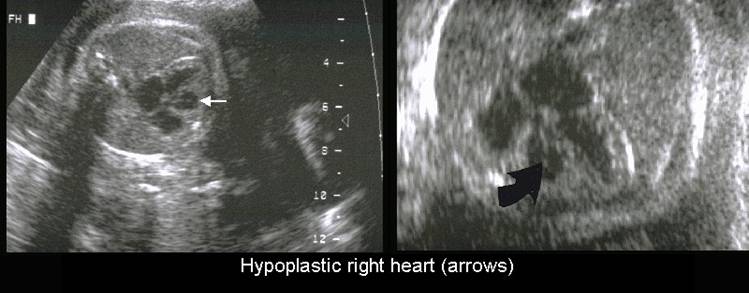
HYPOPLASTIC RIGHT
HEART SYNDROME |
|
|
|
Type I |
Small RV due to competent tricuspid valve (more common). |
|
Type II |
Normal/large RV secondary to incompetent tricuspid valve |
|
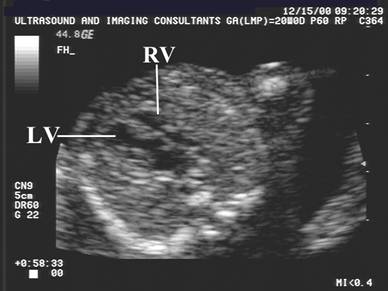
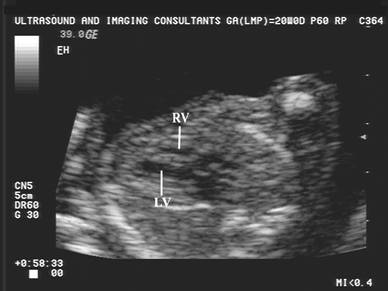
Right Ventricle |
Small cavity in type I / Large if tricuspid incompetence |
|
|
|
|
Pulmonary Artery |
Atresia of the valve |
|
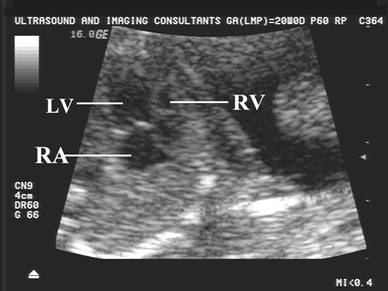
Atrial Septum |
Secundum defect is frequently associated. |
|
Tricuspid Valve |
May be regurgitation resulting in congestive cardiac
failure and hydrops |
|
Tricuspid
stenosis |
Turbulence and increased velocity distal to valve. |
|
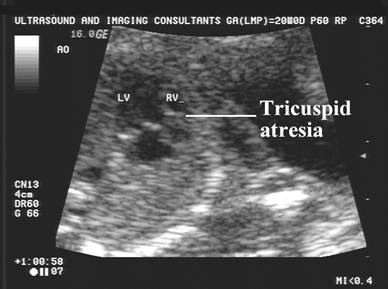
Tricuspid
atresia |
No flow through the valve |
|
|
|
|
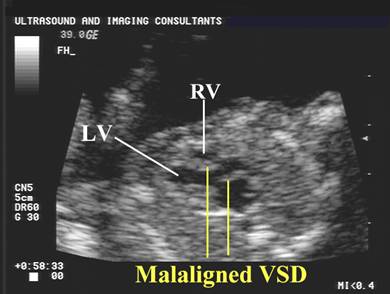
Ventricular
septal defect |
|
|
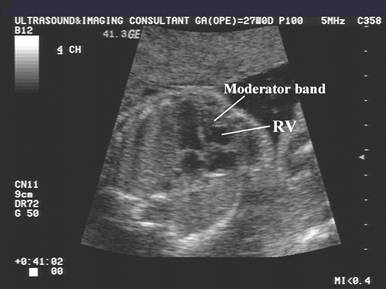
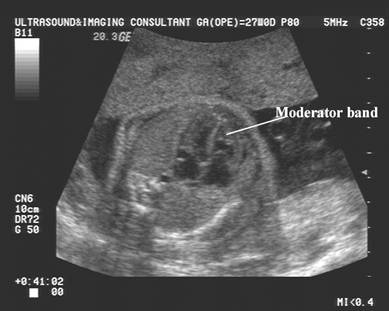
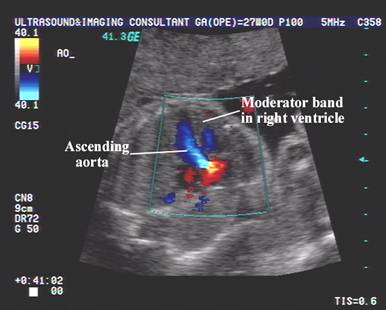
Moderator Band |
Do not confuse a large
prominent moderator band in the right ventricle that appears to result in ventricular disproportion
as a hypoplastic right ventricle. Note the normal tricuspid
valve and normal perfusion of the chamber on color doppler imaging. |
|
|
|
|
|
Video clip of
Hypoplastic Right Heart
|
|
|
|
|
|
HEMODYNAMICS |
There is a left to right atrial shunt through the foramen ovale. There is retrograde
flow through the ductus arteriosus into the pulmonary vascular bed.
PROGNOSIS |
Prostoglandin infusion to keep the ductus open has improved the prognosis.