|
VASCULAR
CALCIFICATIONS IN THE LIVER |
Vascular accidents involving the fetal liver include calcified portal or
hepatic venous clots, and foci of ischemic hepatic necrosis due to
thromboemboli. The literature suggests that vascular insufficiency is the most
frequent cause of hepatic calcifications (1,2).
PATHOGENESIS |
Several possible mechanisms have been proposed:
- Emboli from thrombi in placental veins. Large parietal venous thrombi have been found in the placenta of several neonates with portal vein thrombosis (1).
- Portal vein thrombosis can result from intravascular fibrin formation following maternal or fetal release of thromboplastin, because calcified fibrin thrombi, formed in situ while the fetus was still alive, have been found in autopsies of stillborn neonates (1,2).
- Organ infarction after anemic shock from placental accident and secondary vascular thrombosis (1,3). Clinical evidence to support this is lacking (4).
- Subcapsular calcifications seen on ultrasound support a vascular accident (3). Diffuse involvement indicates ischemic infarction (5).
There is a high association between multiple anomalies and
aneuploidy and hepatic calcifications due to vascular accidents (1,2,5,6).
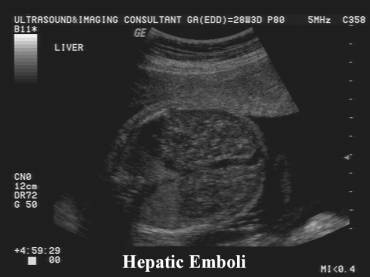
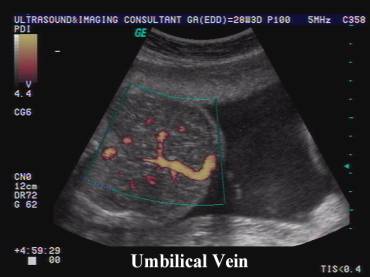
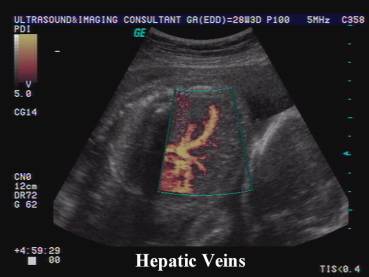
Hepatic
vascular emboli from twin to twin transfusion syndrome
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
REFERENCES |
- Blanc WA, Berdon WE, Baker DH et.al. Calcified portal vein thromboemboli in newborn and stillborn infants. Radiology 1967;88:287-292.
- Friedman AP, Haller JO, Boyer B et.al. Calcified portal vein thromboemboli in infants. Radiology 1981;140:381-382.
- Nguyen DL, Leonard JC. Ischemic hepatic necrosis; a cause of fetal liver calcification. AJR 1986;147:596-597.
- Richards DS, Cruz AC, Dowdy KA. Prenatal diagnosis of fetal liver calcifications. J Ultrasound Med 1988;7:691-694.
- Bronshtein M, Blazer S. Prenatal diagnosis of liver calcifications. Obstetrics and Gynecology 1995;86(5):739-743.
- Hawass ND, El Badawi MG, Fatani JA et.al. Foetal hepatic calcification. Pediatr Radiol 1990;20:528-535.